 1-800-222-0017 (24/7)
1-800-222-0017 (24/7)
 1-800-222-0017 (24/7)
1-800-222-0017 (24/7)

SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC (PV) GRID-TIE FOR MULTI-TENANT BUILDINGS
Net metering or Grid-Tie allows exchanging any surplus energy produced by the PV system for utility energy credits to be used during periods when the PV system is not producing enough energy to meet the needs... This means that the electric meter spins "backwards" when power is flowing from the building to the utility, and spins "forwards" when electricity flowing from the utility into the building... At the end of the month, only the net consumption is billed... It is the amount of electricity consumed, less the amount of electricity produced... The utility acts much the same as a battery, crediting the energy "account" for later use if production exceeds consumption...
For example, during the middle of the day, the system produces three kilowatt-hours but the building uses only one kilowatt-hour... Thus, the "account" will be credited for two kilowatt-hours... Later that evening, two additional kilowatt-hours might be used and the "account" ends up with a net zero balance, owing the utility nothing for that day...
There are three main reasons net metering is important... First, as increasing numbers of primarily residential customers install renewable energy systems in their homes, net metering provides a simple, standardized protocol for connecting their systems into the electricity grid that ensures safety and power quality... Second, as many residential customers are not at home using electricity during the day when their systems are producing power, net metering allows them to receive full value for the electricity they produce without installing expensive battery storage systems... Third, net metering provides a simple, inexpensive and easily administered mechanism for encouraging the use of renewable energy systems, enabling important local, national, and global benefits...
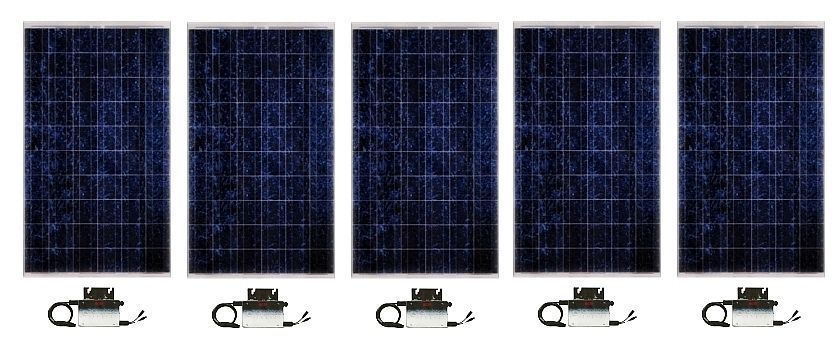
REC SCM215 - 215 Watt solar pv modules & Enphase-Micro Inverters for use in net metering applications: The Enphase Micro-Inverters are a great advancement in solar pv net metering applications... Basically, prior to using micro-inverters, you would have to size a string of modules/panels, number of panels connected in series +&-, and then connect them to dc disconnects and use larger awg wire size to run to a centralized net metering inverter... Also, the centralized inverter, with the use of MPPT, maximum power point tracking, an algorithm used to track the power from an array, would view the entire array as a single panel/module... Meaning, that what ever the lowest power reading it got from all the modules connected to the inverter, it would request that amount of power from all the modules in the array... So if one module/panel is in the shade and not producing it's max power, and all the other modules were producing their max power, the inverter would request the amount of power which the shaded module is producing from every panel in the array (all the panels)... Basically, micro-inverters have made wiring and balance of system components for use in net metering a lot more simplified...
The Enphase Micro-Inverters are basically individual net metering inverters which are connected to each panel and are connected together in a daisy chain... So if you had six panels you would have six micro inverters... The end panel would connect it's dc positive and negative conductors (wires), directly to the it's micro-inverter, and the end panel's micro inverter would connect directly to the micro-inverter of panel next to the end panel, and so on and so on... When you get to the beginning panel of the chain along with it's micro inverter, the ac interconnect cable on the micro-inverter, which is connected to all the micro-inverters from all six panels, will connect to a branch ac circuit, which is then connected to ac junction box, and from there the ac wires from the junction box are sent to the ac distribution box.... By using micro-inverters, each inverter uses the MPPT, maximum power point tracking, algorithm to request the max power from an individual panel and send its power over the ac interconnect cable... By all the panels in the array having an individual inverters associated with them you will get more power out of your array, unlike the centralized inverter which treats the array as a single panel/module...
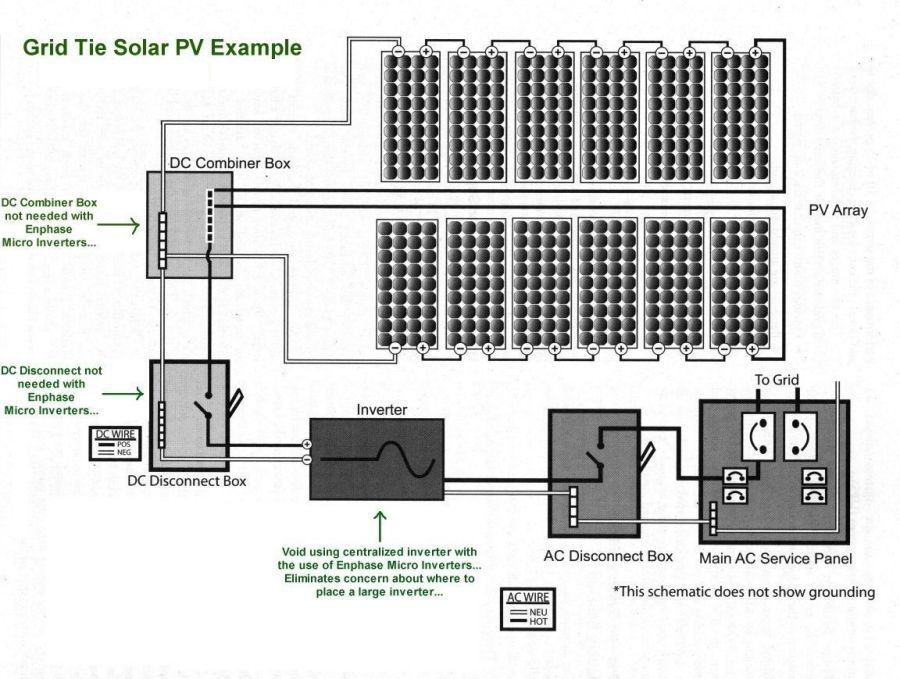
Solar power production is affected by various factors such as module mis-match, obstruction shading, inter-row shading, and obstacles such as dust or debris. In addition, non-uniform changes in temperature, irradiance, and shading create complex current-voltage curves, further affecting energy harvest. This is due to the fact that in traditional systems the performance of the entire system is dictated by the performance of the weakest module.
The Enphase Energy Micro-inverter System solves solar power challenges by performing Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) at each solar module. MPPT is an algorithm used to calculate and respond to temperature and light changes detected on a solar power system, and to determine how much power to draw from the module. In contrast, centralized inverter’s MPPT algorithm sees the entire solar power system as a single module, and responds to the lowest production numbers it detects.
The Enphase MPPT algorithm works at each solar module in an installation and achieves greater than 99.6% accuracy which enables it to maximize energy harvest at all times, even during variable light conditions. Tests show systems using Enphase Micro-inverters increase energy harvest by as much as 25% over systems using traditional inverters.
Traditional centralized inverters implementations create a single point of failure for solar power systems. If the inverter fails, the entire system is disabled. Enphase Micro-inverters convert power independently at each solar module. If one micro-inverter fails, the rest continue to operate as usual. Also, if a micro-inverter is damaged or fails, it can be replaced during routine maintenance or when convenient, further reducing maintenance costs.
![]()
ENPHASE MICRO-INVERTERS AND MULTI-TENANT BUILDINGS

With the new incentives available today there has never been a better time to install solar... Incentives are provided by city, state, and federal programs in the form of rebates, tax credits, tax deductions, and depreciation allowances...
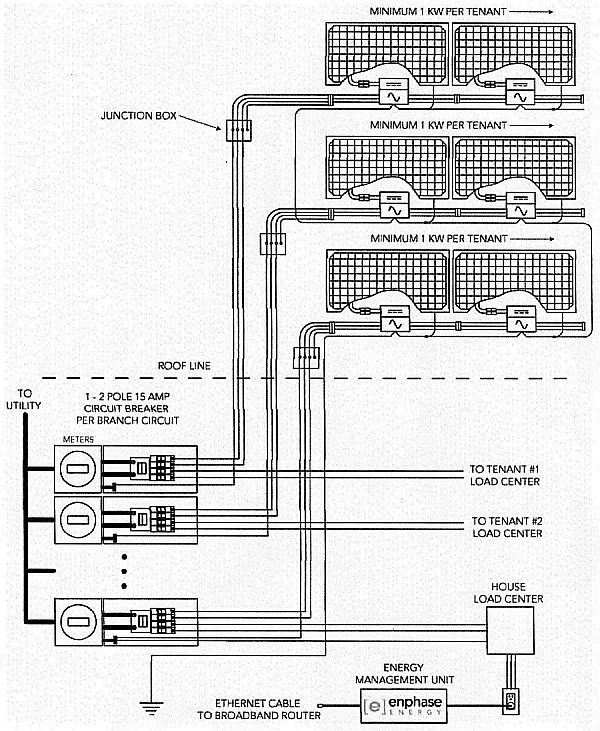
Installing individual Photovoltaic systems for each tenant has been very challenging prior to the availability of the micro-inverter... A string inverter, large centralized inverter, requires that a number of PV modules be connected in series in order to satisfy the input voltage requirements of the inverter... (Series refers to connecting the panels together plus wire to negative wire and negative wire to plus wire to increase the system voltage... String refers to a number of panels connected together in series, in example, 5 panels connected together in series wiring... Series wiring increases volts produced by the panels...) The length of these series strings could be 8 to 12 modules depending on the module selected... Shading any portion of the series string reduces the output, of the entire string dramatically... String inverters smaller than 2000 watts are not available, so providing individual systems for each tenant would require considerable amounts of roof space...
The Enphase Micro-Inverter System provides a number of advantages... The concept of one inverter per PV module allows each PV module to be power tracked individually... This enables PV modules to be installed in all the available roof space without the usual shading constraints... This provides the maximum flexibility when designing the system since any amount of modules per tenant can now be supported...
The Enphase Micro-Inverter system enables solar pv net metering for apartment buildings because:
- Systems can be designed and installed for multiple solar pv net metering system sizes, including very small systems...
- Solar pv modules can be installed on multiple roof planes, thereby maximizing roof space...
- Effects of shading (a particular problem with dense urban areas) are greatly reduced...
- Limited space to locate a large centralized string inverter is not an issue since micro-inverters are located beneath each solar pv module...
Insure array, group of modules connected together, sizes meet minimum requirements: Rebate programs often have minimum size requirements for solar pv arrays... For example, to participate in the California Solar Initiative (CSI) rebate program, the minimum size for each system is 1 kW / CEC-AC...
Communications and Monitoring Considerations: The Enphase Envoy gateway is a data logger / Internet gateway for the micro-inverters in the Enphase micro-inverter system... Envoy Communications Gateway consists of the EMU, Energy Management Unit and Enphase Enlighten website... The micro-inverters communicate performance and production data over the AC power-line to the EMU... The EMU simply plugs into any 120 VAC receptacle inside the building and then connects to a broadband router, will take up space on the router reserved for a cpu, and will forward the data collected about the micro-inverters to the Enphase server... To access the information you will need to log on to the Enphase Enlighten website... Enphase recommends that the EMU be connected as close to the meter stack... In placing the EMU as close as possible to the meter stack improves signal strength from the micro-inverters to the EMU...
![]()
![]()
For shipping and handling costs please inquire within or call 1-800-222-0017 and ask for Ben...
PLEASE ALLOW UP TO 10 BUSINESS DAYS OR SOONER FOR DELIVERY DUE TO GLOBAL DEMAND FOR THIS PRODUCT...
Note: We Export, inquire within @ 1-800-222-0017 (27/7) (US and International Toll Free Number...)
![]()
![]()
Greenpower Global Technology, Inc.
1172 South Dixie Highway / Unit 615 / Coral Gables, Florida 33146 / USA
1-800-222-0017
US and International Toll Free Number
e-mail to: greenpower@solarpath.com
1-305-665-4212 (FAX)